
Feeling healthy, fit and energized is directly influenced by your lifestyle and nutrition. To boost your metabolic health, we created this unique range of clean and balanced supplements. For mental or physical performance, immunity, strength, energy, weight loss, cardiovasculair or joints. Every product unique science based and all natural.
If you’re aiming to get all the right nutrients to help you feel great and perform at your best, then check out our supplements. Unique formulations that really work. Developed by our Swiss research team. To deliver scientifically proven results. We use only high-quality essential and protective ingredients. Natural and powerful antioxidants for more energy and vitality.










We all know that our bodies need nutrition, and not just for plain energy. We also need a wide range of micronutrients to function well. Ideally, we should get this from a healthy and varied diet, but we don’t always manage that. Vitamins and supplements can be a good way to make sure you get all the nutrients you need.
In this article:
‘Supplement’ means “a thing added to something else in order to complete or enhance it,” and that is exactly what a nutritional supplement is intended to do for your diet. It can be of use in case of deficiencies and for optimization. Supplements should never be a substitute for healthy food and living.
Some situations may call for certain supplements. For instance, Vitamin D3 supplementation is indicated for people living in in temperate and cold climate zones during winter time. Vitamin D3 is produced through sun exposure, which is insufficient under those circumstances.
There are two sorts of supplements: food supplements, such as our Go-Keto MCT Oil or protein shakes, which contain relatively high concentrations of specific nutrients, but you consume them just like regular food or drinks.
The other type of supplement usually comes in the form of tablets, capsules, powder or drops that are meant to be taken separately, on top of your regular meals. Such supplements usually contain concentrations of specific (micro)nutrients that are higher than those found in food.
Strange but true: vitamins weren’t ‘discovered’ until the early 1900’s, when scientists found out that there are diseases that are caused by nutritional deficiencies. Most credits go to biochemist Casimir Funk, who not only gave vitamins their name in 1912, but also linked a number of diseases to the missing substances, among them scurvy (Vitamin C); beriberi (Vitamin B1) and rachitis (Vitamin D). It took until 1948 to complete the whole list of Vitamins as we know it.
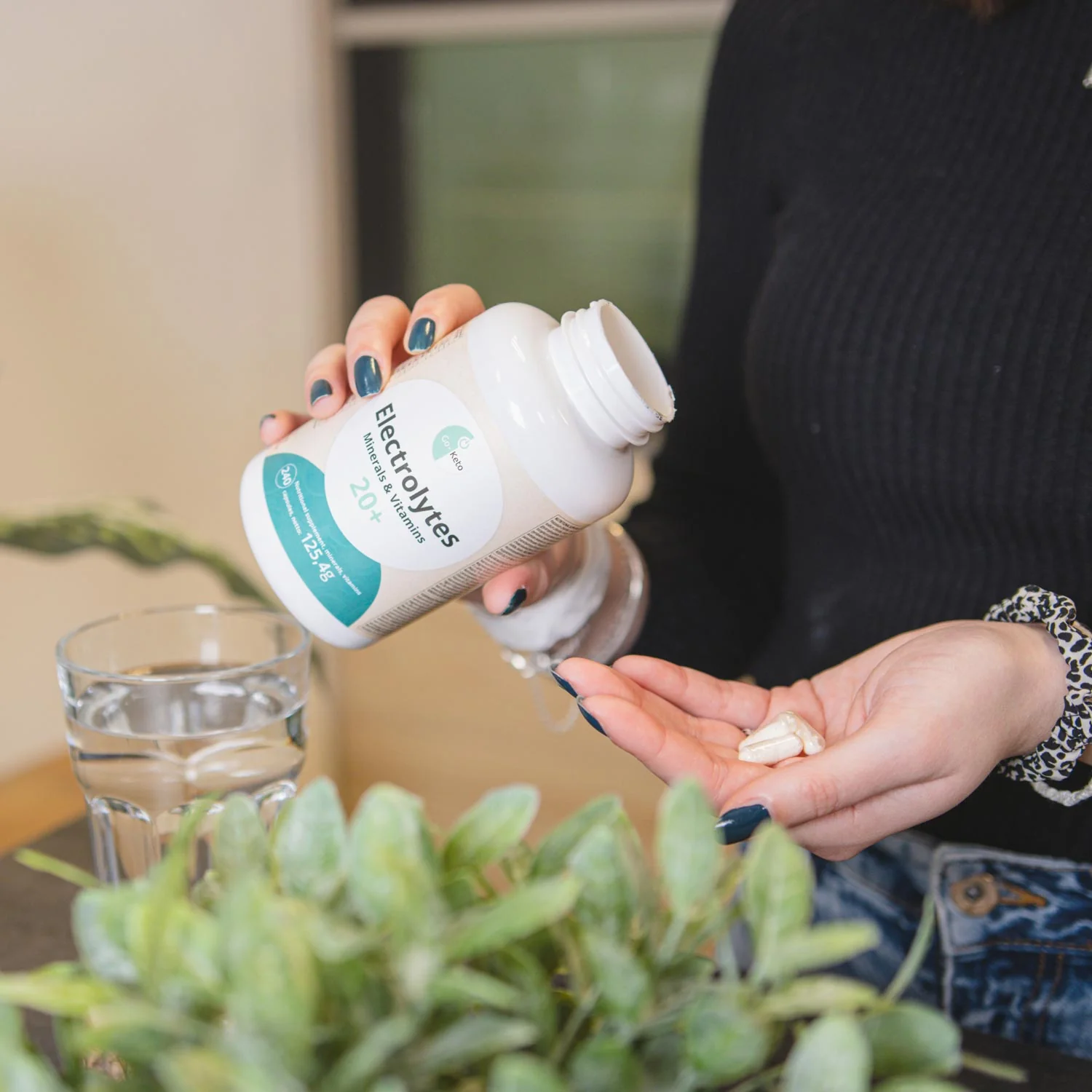
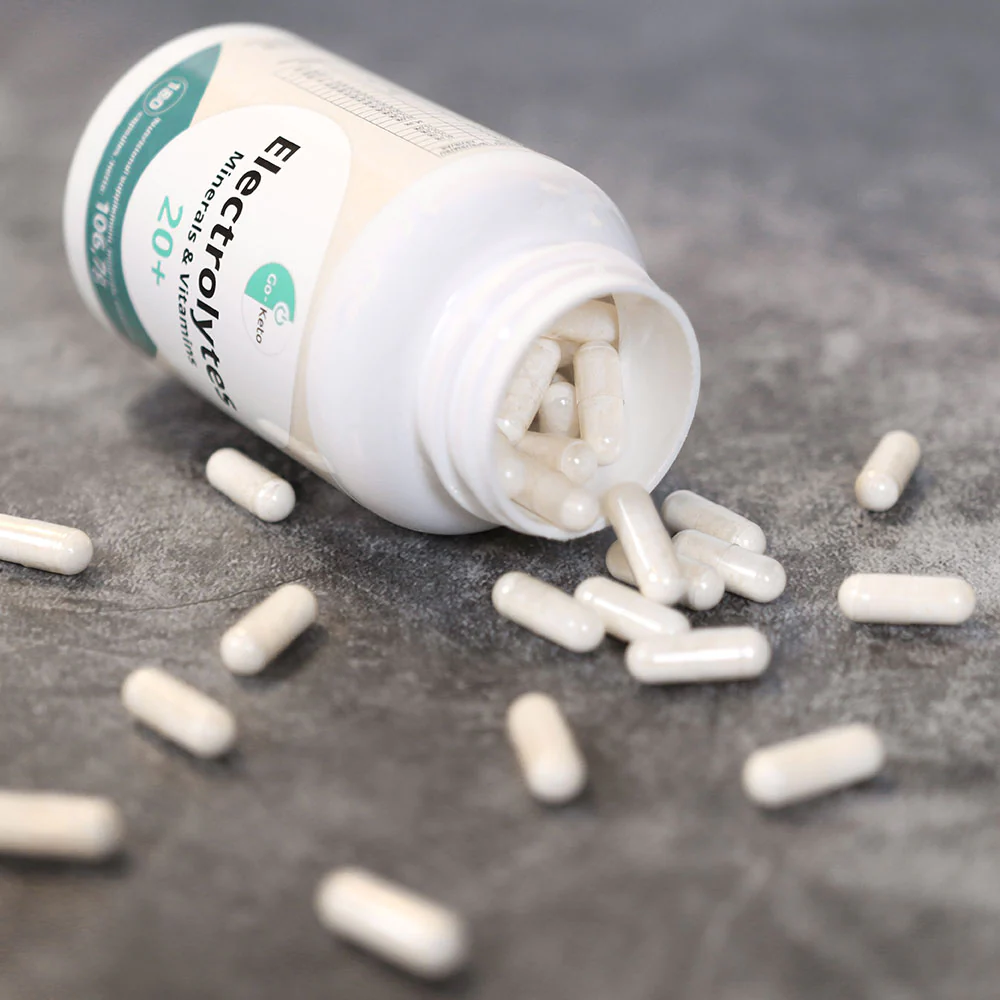
The term ‘multivitamin’ is not quite precise, because this type of supplement usually contains a variety of micronutrients, including minerals, and not just vitamins. Our Go-Keto Electrolytes 20+ supplement contains a very wide range of over 20 supplementary micronutrients, with a focus on the electrolytes that are so important for keto and low carb diets.
A fair question. After all, food contains all the nutrients we need, right? Well, in theory, it does, but in practice, it can be hard to get a sufficient daily intake of micronutrients from your diet. And that’s not just because a busy, stressful life and a healthy and balanced diet don’t go together all that well.
Even though there’s no scarcity of food in our western society, nutritional deficiencies are much more common than you would expect. Did you know, for instance, that about 15 to 30% of the people Europe have a slight to moderate magnesium deficiency [1,2]?
As a result of modern intensive, mechanized agriculture, food (unless it’s organically grown) nowadays contains much less minerals and other micronutrients than in our grandparents’ day [3]. Getting all the necessary nutrients from food takes conscious choices and effort. Meanwhile, statistics show that we eat more and more processed and refined food, still increasing the risk of deficiencies.
Besides vitamins and minerals, vegetables and fruit – provided they’re not too depleted or processed – contain yet another type of micronutrient: phytonutrients.
These are chemical substances produced by plants to protect them against “attackers” such as mildew, bugs and disease. In the human body, they also trigger useful reactions. They may act as antioxidants, dealing with free radicals that may cause cellular and tissue damage, and can reduce inflammation.
So far, about 25.000 phytonutrients have been identified; the sub-group called polyphenols is perhaps the most important. Well-known polyphenols are Resveratrol and OPC’s. The broadest range of polyphenols is found in grapes (Vitis Vinifera).
The Polyphine® used in our Resveratrol, OPC, CoQ10, Polyphine is extracted from French grapes, including the seed, stem and skin, to give you the full range and benefit of the polyphenols.
Polyphine® is also used in Good for JOINTS with Glucosamine and Vitamin D, so that it contains not only the building blocks for bones, joints, cartilage and ligaments, but also a powerful agent to tackle the inflammation that’s often at the root of joint pain.
The components of supplement listed above can be synthetic – made in a laboratory, like chemicals – or natural in origin. Natural vitamins, minerals and other ingredients are extracted from natural sources. Omega-3 supplements, for instance, can only be obtained from natural sources like fish or krill. At Go-Keto, we focus on natural, bio-organic and sustainable sourcing for our supplements’ ingredients.
Supplements may also contain extracts of specific plants and herbs, like curcuma, milk thistle, grapes etc., because of the important phytonutrients they contain. Well-formulated natural supplements contain ingredients selected for best bio-availability, i.e. you can easily absorb and use them.
There are circumstances which can diminish our ability to absorb nutrients from food or increase our need for them, such as:
Certain groups, like small children, adolescents, pregnant women and aging people, are also advised to take specific supplements in order to function optimally and avoid deficiencies.
The general advice of health institutions is to focus on getting a sufficient intake of the nutrients for which deficiencies are most common. These are: Vitamins A, B11 (folic acid), D3, B12; the minerals magnesium, iron, zinc and calcium, plus, last but not least, Omega-3 DHA/EPA.
Our body can’t produce EPA and DHA, so we need to get these important Omega-3’s from our food or through a supplement. They support (250mg daily):
To get your Omega-3 through food, you would need to eat fatty fish 1-2 times a week. If that doesn’t work for you, opt for a top quality Omega-3 supplement like our Krill Oil Omega-3 Superba Boost. Don’t forget to check the advantages that krill oil has over fish oil!
Subscribe to our newsletter for latest insights and exclusive offers.